Table of Contents
Growing up, we’ve all heard the tale of the tooth fairy leaving money under our pillows. (Apparently, you can be financially compensated for losing teeth as a child-not sure why it doesn’t apply to the elderly but ok). Anyway, to qualify for the magic money, you need a tooth to prove that you’ve lost baby teeth, but imagine a scenario where you don’t need to provide a tooth, just teeth in your mouth to verify that you still have teeth and thus qualify for the monetary benefit?
Staking allows for something like that.
To make sure transactions are legitimate, every transaction needs to be validated by users. There are two ways of doing this: staking and mining, but we’ll be focusing on staking today.
Think of staking like a security deposit, where putting your crypto out to forge blocks in the blockchain (valid transactions) can entitle you to some form of compensation. The more you stake the more likely you are to be chosen to forge a block and being chosen will grant you a reward in extra coins.
Why stake?
Staking is an easy way to earn interest on your cryptocurrency holdings.
- No equipment is needed for crypto staking, unlike crypto mining.
- You’re helping to maintain the security and efficiency of the blockchain.
- Profitable way to invest your money. And, the only thing you need is crypto that uses the proof-of-stake model.
Think of it this way, staking is one way of making your assets work for you.
Risks and drawbacks
Even leaving your money in the bank has its risks, so here are some things to note when it comes to staking.
- Impermanent loss: Crypto prices are volatile and can drop quickly. If your staked assets suffer a large price drop, that could outweigh any interest you earn on them.
- Slashing: If a validator misbehaves (e.g. goes offline, attacks the network, or runs modified software. In this case, a validator forfeits a defined proportion of staked tokens
- Smart Contract risk: Like any other software code, smart contracts are susceptible to cyber-attacks and technology failures.
- Illiquidity:The staking mechanism also involves the withdrawal of an asset from circulation, blocking funds in the wallet. During that period, you’re unable to do anything with your staked assets such as selling them. This means that the user is illiquid. As seen with what happened with UST and LUNA, people who staked LUNA would not have been able to unstake, withdraw and sell to cut losses.
A big problem with staking is the long lock-up of funds, which renders many illiquid – for example, there is currently around US$26 billion staked with Ethereum, but it not known when one can unstake those tokens. This is where liquid staking – which allows users to stake (and unstake) any amount of ETH with no lock-up period – is game-changing.
Having your cake and eating it
Liquid Staking allows users to delegate their tokens to a service that stakes without them losing access to their funds. The funds remain in escrow but aren’t “locked”, unlike PoS staking. The trade-off? A lower APR/APY, but it is a small price to pay for such flexibility.
The market leader in the space is Lido, a liquid staking solution for Ethereum. Currently holding 17.5% of the entire staked ETH supply, Lido has undeniable dominance on Ethereum.
How it works is that when you stake your ETH, you get back something that is supposed to be the same – in the case of Lido, stETH – a tokenized version of the staked funds, which can be transferred, stored, spent or traded as one would a regular token.
How liquid staking works
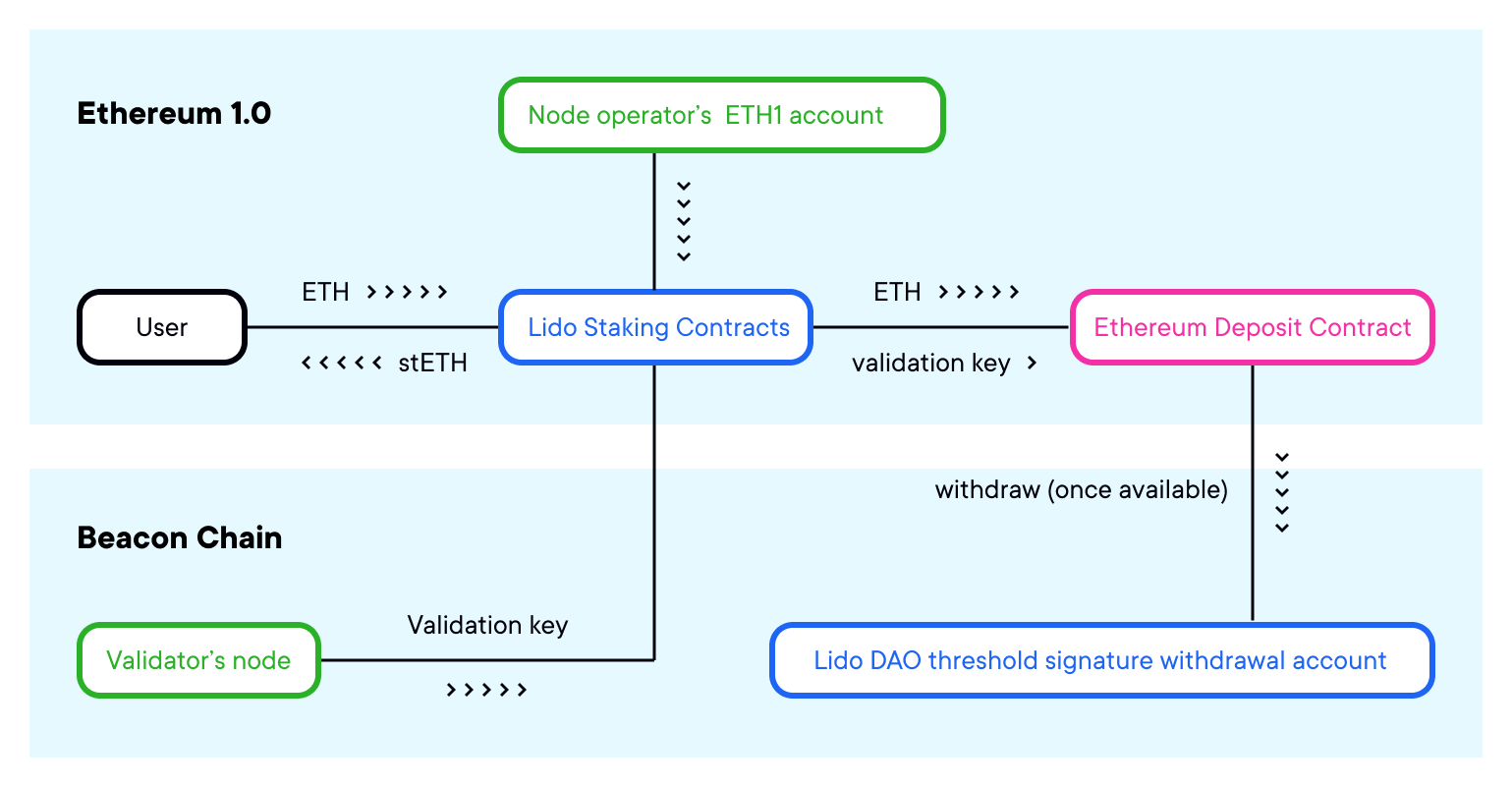
Image: Lido
- A user would deposit their ETH into a third-party application.
- This app would deposit this user’s ETH into the Ethereum deposit contract for them (through the use of running their own validators), and in return would mint a representative ETH token for them (eg. stETH).
- stETH will allow users to maintain their ETH liquidity. stETH can also be used for lending, collateral and more, while still earning daily staking rewards.
- Ustake anytime through the use of stETH-ETH liquidity pools.
- Once transactions are enabled on Ethereum in a future upgrade, this representative ETH will then be returned back to the third-party issuer.
- The issuer will then give the user back an equivalent amount of ETH to their original stake, along with the rewards earned while securing the network.
Future of Ethereum Staking

The news of Ethereum 2.0 took the crypto world by storm as it signaled Ethereum’s transition to a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism. Validators can stake their ETH on the Beacon Chain to secure the blockchain and earn staking rewards in proportion to the amount of tokens staked.
To become a full validator and stake on Ethereum 2.0, you need 32 ETH (currently over US$60,000). Not many people can do that, posing a financial barrier. Additionally, those who stake their ETH into the Ethereum deposit contract cannot unstake their funds until transactions are enabled. Since there is no official date set for this phase of the upgrade, it might be years until users can get back their staked ETH. With such a long and uncertain waiting time, many people are not incentivised to stake their ETH.
Liquid staking is an innovative alternative to bypass risks associated with illiquidity, complexity and centralization, though other staking risks remain.
Liquid staking manages to circumvent the firm requirements that prohibit staking on the Ethereum network. Smaller wallets can stake and unstake any amount of Ethereum and larger holders can use liquid staking services to hedge their funds against ETH volatility. Essentially, this endeavor is a step closer to greater accessibility as it allows for all parties to stake without the requirement of maintaining complex staking infrastructure.
Making it possible to stake and still use of your tokens should make it a whole lot more attractive for people to stake. As Ethereum moves towards its long-awaited Consensus Layer upgrade, Ethereum liquid staking providers will no doubt gain more attention.
With all the developments in the space, institutional investment and overall interest in DeFi, Liquid staking primed to grow in parallel with the greater DeFi movement.










